why do somatic cells divide Meiosis occurs in reproductive cells while mitosis occurs in somatic
Have you ever wondered why cells divide? It’s a crucial process that allows living organisms to grow and repair damaged tissues. There are two main types of cell division that occur in the human body: meiosis and mitosis. While both processes are essential for life, they have some key differences. Meiosis occurs in reproductive cells, such as sperm and egg cells. Its main purpose is to produce haploid cells, which have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This is necessary for sexual reproduction, as it allows for genetic diversity in offspring. Meiosis consists of two rounds of division, resulting in four haploid cells. On the other hand, mitosis occurs in somatic cells - that is, all cells in the body except for reproductive cells. Its primary function is to produce two identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This is necessary for growth and repair of tissues, as well as for asexual reproduction in some organisms. Mitosis consists of four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. To better understand how these processes occur, let’s take a look at two images. The first image shows the stages of mitosis, with each stage labeled and described. After interphase, during which the cell prepares for division, the cell undergoes prophase, where the chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes. The chromosomes then align at the cell’s equator during metaphase, before being pulled apart by spindle fibers during anaphase. Finally, the cell divides into two daughter cells during telophase. [image 1 - mitosis stages]
Stages of Mitosis
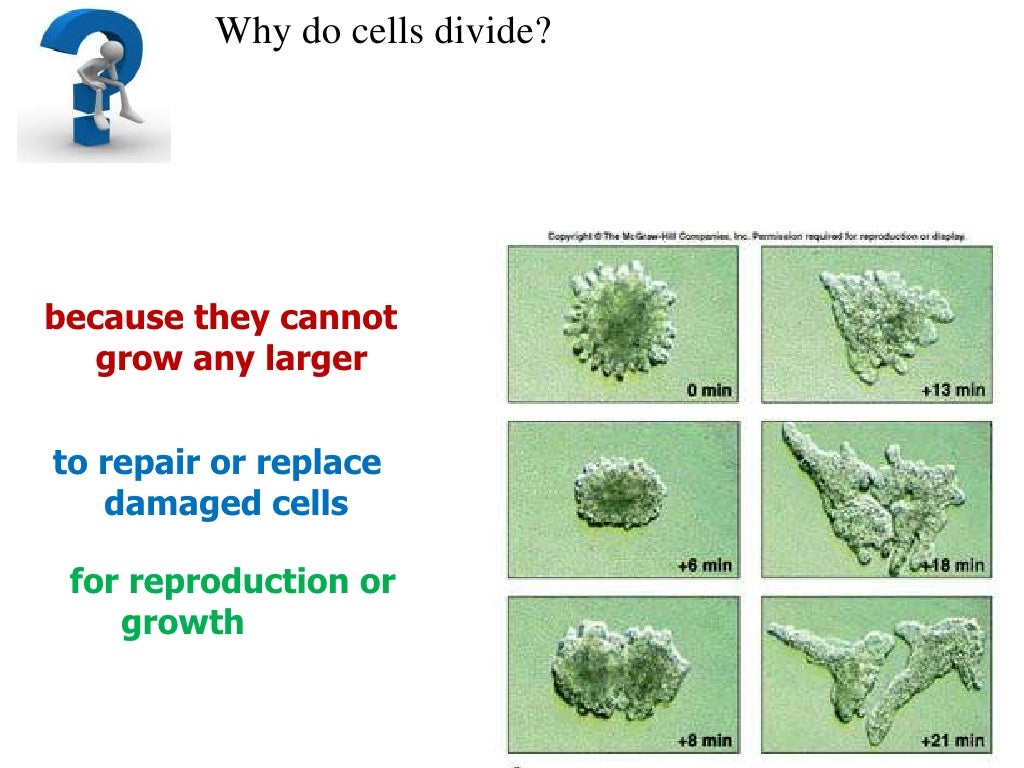 Image source: slidesharecdn.com
Image source: slidesharecdn.com
The second image shows the stages of meiosis, both meiosis I and meiosis II. Meiosis I separates homologous chromosomes, while meiosis II separates sister chromatids. These processes help ensure genetic diversity in offspring. [image 2 - meiosis stages] Stages of Meiosis
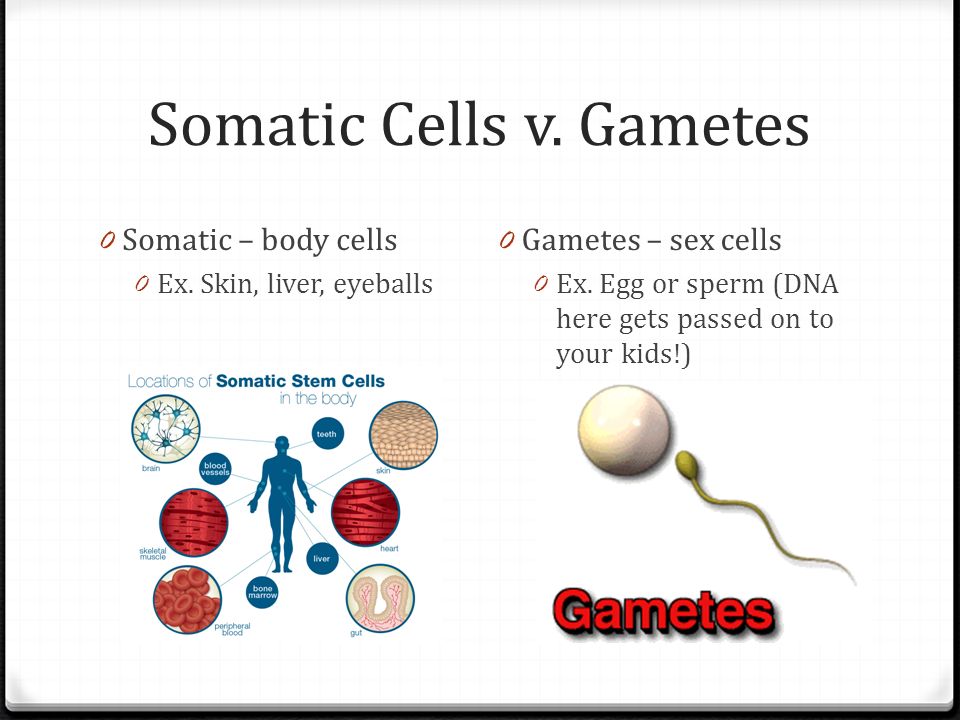 Image source: useruploads.socratic.org
Image source: useruploads.socratic.org
So there you have it - a brief explanation of the differences between meiosis and mitosis. Both processes are essential for life as we know it, and they help ensure genetic diversity and proper tissue growth. Keep in mind that this is just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to cell division, but hopefully this information has piqued your curiosity about the fascinating world of biology. If you are searching about Why do Cells Divide? you’ve visit to the right place. We have 5 Images about Why do Cells Divide? like Meiosis occurs in reproductive cells while mitosis occurs in somatic, Biology Unit 4: Cell Cycle & Cell Division Basics Notes and also Why Do Cells Need to Divide - Pediaa.Com. Here you go:
Why Do Cells Divide?
 www.slideshare.netwhy divide cells
www.slideshare.netwhy divide cells
Why Do Cells Need To Divide - Pediaa.Com
 pediaa.commitosis divide fasi microscopic mitosi microscopio cellule tissues microscopes brightfield medienbildung prophase metaphase telophase meristem anaphase cellulare pediaa lernpfad ciclo
pediaa.commitosis divide fasi microscopic mitosi microscopio cellule tissues microscopes brightfield medienbildung prophase metaphase telophase meristem anaphase cellulare pediaa lernpfad ciclo
Meiosis Occurs In Reproductive Cells While Mitosis Occurs In Somatic
 socratic.orgsomatic cells reproductive meiosis occurs mitosis meaning socratic while word inheritance
socratic.orgsomatic cells reproductive meiosis occurs mitosis meaning socratic while word inheritance
Biology Unit 4: Cell Cycle & Cell Division Basics Notes
 www.slideshare.netdivide
www.slideshare.netdivide
Why Do Cells Need To Divide - Pediaa.Com
 pediaa.comwhy cells divide need cell division pediaa
pediaa.comwhy cells divide need cell division pediaa
Why do cells divide?. Why cells divide need cell division pediaa. Meiosis occurs in reproductive cells while mitosis occurs in somatic